- Home
- Posters for Intestinal Inflammation

Ribotype 027 is Associated with Increased Lactoferrin and Toxin in Patients with Clinically Defined C. difficile Disease

Evaluation of Fecal Lactoferrin, CRP and Clinical Activity Indices for Assessing the Presence of Intestinal Inflammation in IBD and IBS Patients Classified by Ileocolonoscopy

Comparison of CRP, Clinical Activity Indices and Fecal Lactoferrin with Disease Status in Ileocolonoscopy of Patients with IBD and IBS

A Comparison Among Four Neutrophil-Derived Proteins in Feces as Indicator of Disease Activity in Ulcerative Colitis

Serial Fecal Lactoferrin Measurements are Useful in the Interval Assessment of Patients with Active and Inactive Inflammatory Bowel Disease

Evaluation of Fecal and Serum Anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae Antibodies (ASCA) as an Aid in the Diagnosis of Crohn’s Disease

Fecal Lactoferrin: Sensitive Marker for Monitoring Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)

Clinical Evaluation of the IBD-CHEK® Test for Detecting Elevated Fecal Lactoferrin as an Indicator of Intestinal Inflammation in Pediatric Patients

Fecal lactoferrin in newborns, infants and toddlers- Evaluation in asymptomatic children and patients with functional disorders

Fecal ASCA Measurements in the Assessment of Pediatric Patients with Crohn’s Disease (CD) or Suspected Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)

The Detection of Lactoferrin, ASCA and ANCA in Feces is useful for Assessing Pediatric IBD Patients

Measurement of Anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae Antibodies in Human Feces as an Indicator of Crohn’s Disease

Evaluation of Fecal Biomarkers for Monitoring Antibiotic Treatment of a Patient Infected with Clostridium difficile
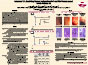
Comparison of CRP, Clinical Activity Indices and Fecal Lactoferrin with Disease Status in Ileocolonoscopy of Patients with IBD and IBS

Evaluation of CRP, Fecal Lactoferrin and Clinical Activity Indices for Assessing the Presence of Intestinal Inflammation in IBD and IBS Patients

Lactoferrin as a Predictor of Disease Severity for Clostridium difficile Disease

Tables for Lactoferrin IBD Mucosal Healing

Fecal Lactoferrin in Children with Gastrointestinal Symptoms

Fecal Lactoferrin as an Indicator of Intestinal Inflammation in Patients with Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea

Fecal Lactoferrin, Calprotectin, PMN-Elastase, CRP and White Blood Count as Indicators for Mucosal Healing and Clinical Course In Ulcerative Colitis: A Prospective 12-Month Monitoring Study
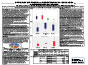
Efficacy of Faecal Lactoferrin in IBS & IBD: A Comparative Study

Evaluation of the LEUKO EZ VUE® for Measuring Fecal Lactoferrin as a Marker of Intestinal Inflammation

Fecal Lactoferrin, Calprotectin, PMN-Elastase, CRP and White Blood Count as Indicators for Mucosal Healing and Clinical Course in Ulcerative Colitis: A Prospective 12-Month Monitoring Study

Feasibility and Utility for Long-Term Monitoring of Fecal Lactoferrin in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis

Fecal Lactoferrin: Reliable Inflammatory Marker in Pediatric IBD

Hospitalized Patients with Ribotype 027 Clostridium difficile Infection and Stool Cytotoxicity Have More Severe Disease with an Increased Risk of Death

Fecal ASCA Measurements in the Assessment of Pediatric Patients with Crohn’s Disease (CD) or Suspected Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
